Top Flow Control Valve Types Explained for Efficient Fluid Management?
In the realm of fluid management, flow control valves are crucial components. Experts estimate that nearly 25% of energy is wasted in fluid systems due to inefficient flow regulation. The right valve choice can significantly impact system performance. According to Dr. Samuel Grayson, an industry authority, "Selecting the proper flow control valve can enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs."
Different applications require various types of flow control valves, often leading to confusion. Each type, whether globe, ball, or gate valve, serves distinct purposes. The choice hinges on factors like pressure, temperature, and flow rate. Nevertheless, many systems still utilize outdated valves, leading to suboptimal performance.
The challenge is to navigate these options effectively. Achieving efficient fluid management demands continuous learning and adaptation. While resources exist, they can be overwhelming. Dr. Grayson emphasizes the importance of ongoing education in this field. Ultimately, understanding flow control valves and their proper applications is vital for success.

Types of Flow Control Valves: Overview and Applications
Flow control valves are essential in managing fluid systems efficiently. Understanding the different types is crucial for any industry reliant on fluid management. Common types include gate valves, globe valves, and needle valves. Each serves a distinct function. Gate valves are great for open/close operations, while globe valves provide better throttling accuracy. Needle valves allow for fine adjustments in flow rate.
A study by the International Society of Automation highlights that the correct choice of flow control valve can improve system efficiency by up to 20%. This can lead to substantial energy savings and reduce operational costs. However, many industries still fail to select suitable valves, leading to inefficiencies.
Tips: Always match the valve type to your system's requirements. Avoid trial and error in selection. Ensure your team understands how each valve operates. Remember, even minor adjustments can significantly impact flow dynamics. Don't overlook the importance of regular maintenance to prevent wear and tear on valves. This can save costs in the long run and prolong equipment life.
Top Flow Control Valve Types Explained for Efficient Fluid Management
This bar chart illustrates the various types of flow control valves and their respective applications in fluid management. Understanding the distribution of these valves can help in selecting the right type for specific needs.
Key Specifications and Standards for Flow Control Valves in Industry
Flow control valves play a crucial role in preventing excess fluid movement. In various industries, these valves help maintain system efficiency. They must meet specific industry standards to ensure safety and performance. Common specifications include pressure ratings, temperature ranges, and materials of construction. These factors affect durability and compatibility with different fluids.
When selecting a flow control valve, it is essential to consider the intended application. For instance, valves used in high-temperature environments require specialized materials. Additionally, compliance with standards such as ANSI or API can be vital for quality assurance. Some industries may overlook these specs, which can lead to failures and costly downtime.
An important aspect often missed is the installation process. Improper installation can compromise valve performance. It is critical to ensure that valve orientations and connections are correct. Regular maintenance also helps identify potential issues before they escalate. Awareness of these details can significantly improve fluid management and system reliability.
Top Flow Control Valve Types Explained for Efficient Fluid Management
| Valve Type | Applications | Key Specifications | Industry Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| Globe Valve | Flow regulation, throttling | Pressure rating: PN 16 - PN 40 | API 600, ASME B16.34 |
| Ball Valve | On/off control, quick shut-off | Temperature range: -29°C to 200°C | API 608, ISO 17292 |
| Butterfly Valve | Large volume flow control | Diameter range: 2" to 48" | API 609, MSS-SP-67 |
| Check Valve | Prevent backflow | End connections: Flanged, Welded | API 594, ASME B16.5 |
| Pressure Relief Valve | Overpressure protection | Set pressure: Adjustable up to 300 psi | ASME Section I, API 520 |
Advantages of Utilizing Electronic vs. Manual Flow Control Valves
When considering flow control valves, the choice between electronic and manual options is crucial. Electronic flow control valves provide automation and precision. They can be programmed to respond to specific conditions, adjusting flow rates automatically. This capability can lead to better efficiency and reduced waste. However, they may require complex setups and maintenance. The initial costs can also be higher compared to manual valves.
On the other hand, manual flow control valves offer simplicity and reliability. Operators can directly adjust the flow, which allows for immediate changes as needed. This approach is straightforward, ideal for small operations or temporary setups. Yet, the manual method can lead to human errors and inconsistencies. It requires constant monitoring, which can be labor-intensive.
Balancing the pros and cons of each type is essential. Electronic valves can improve long-term performance, but they need careful handling. Manual valves are easier to manage but might not provide the same efficiency. In some cases, hybrid systems combining both types could be the best solution.
Impact of Flow Control Valve Selection on System Efficiency and Cost
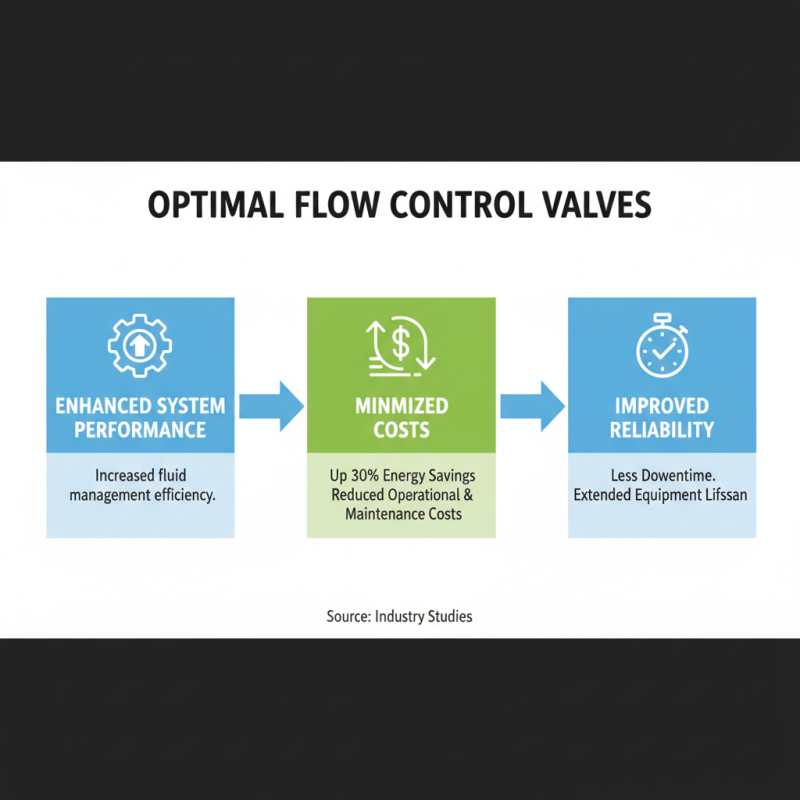
The selection of flow control valves plays a critical role in the efficiency of fluid management systems. An optimal valve can enhance system performance while minimizing costs. According to industry studies, using the right flow control valve can lead to energy savings of up to 30%. This efficiency not only lowers operational costs but also reduces maintenance frequency.
However, choosing the wrong valve can have adverse consequences. Poor flow control can cause pressure drops, leading to increased energy use and wear on equipment. Reports indicate that improper valve selection results in 20% higher operational costs over time. This highlights the need for careful evaluation during the selection process.
Tips: Always assess the specific requirements of your system. Take into consideration factors like pressure, temperature, and fluid type. Regularly review valve performance to ensure ongoing efficiency. A valve that works well today may not be suitable tomorrow. Stay informed about new technologies and innovations in flow control to maintain optimal system performance.
Emerging Technologies in Flow Control Valve Design and Functionality
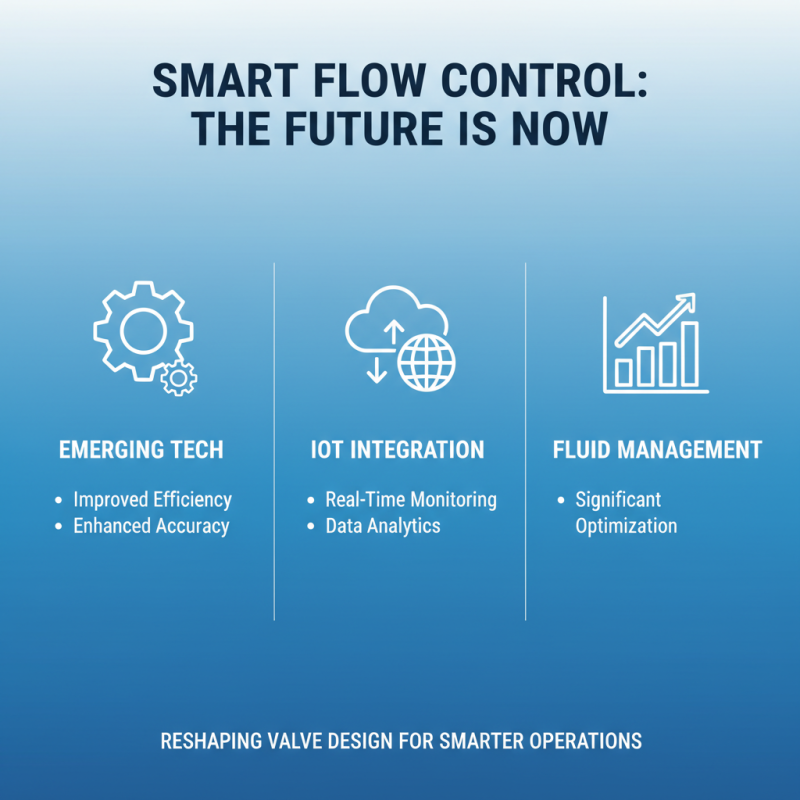
Emerging technologies are reshaping flow control valve design. These innovations focus on improving efficiency and accuracy. Smart flow control valves now integrate IoT capabilities. They enable real-time monitoring and data analysis. This can lead to significant improvements in fluid management.
3D printing is another game-changer. It allows for rapid prototyping of valve designs. Engineers can test multiple configurations quickly. This leads to more tailored solutions for specific applications. However, not all designs will succeed on the first attempt. Iterative testing remains vital in perfecting these technologies.
Another exciting development is the use of advanced materials. Composite materials enhance durability while reducing weight. This can improve performance in various environments. Still, challenges exist in material compatibility and degradation. Ongoing research will address these concerns. Adapting to these new technologies is essential, yet it may require reevaluation of existing systems.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Importance of Flow Control Valves in Modern Industrial Applications
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Automatic Valves in Modern Plumbing Systems
-

2026 Top Valve Actuator Types You Should Know?
-

2026 Best Electric Valves for Efficient Fluid Control?
-

10 Essential Tips for Selecting the Right Control Valve for Your System?
-
How to Locate and Use a Natural Gas Shut Off Valve Safely
