What is a Gas Valve and How Does it Work in Your Heating System
Gas valves play a critical role in the efficiency and safety of heating systems, acting as the control mechanisms that regulate the flow of gas to burners. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, approximately 50% of energy consumption in homes is attributed to space heating and water heating, with gas appliances being a significant contributor. Properly functioning gas valves are essential to ensure that fuel flow is optimized, thereby enhancing energy efficiency and reducing utility costs.
In recent years, advancements in gas valve technology have led to improvements in safety standards and operational efficiency. Data from the American Gas Association indicates that modern gas valves, particularly those with electronic controls, can provide better modulation of gas flow, responding more accurately to temperature requirements in real time. This not only minimizes energy waste but also prolongs the lifespan of heating equipment. Understanding the function and mechanics of gas valves is vital for homeowners and technicians alike, as regular maintenance and timely replacements can significantly impact the overall performance and safety of heating systems.
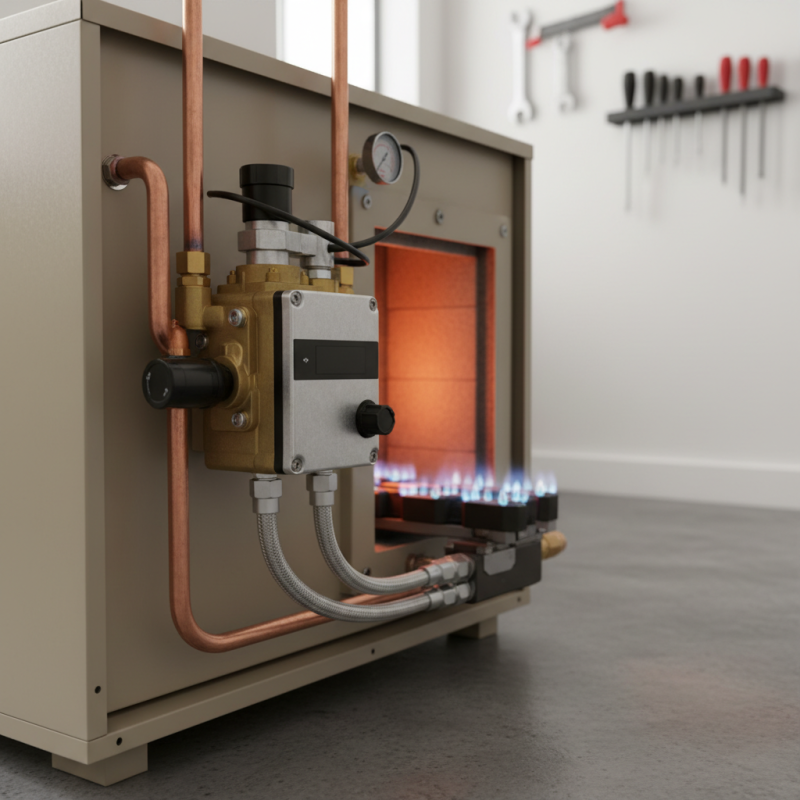

What is a Gas Valve? An Overview

A gas valve is a critical component in heating systems, playing a pivotal role in the control and distribution of gas to various appliances. Functioning as a gateway for gas flow, it ensures that the right amount of gas reaches the burner, which is essential for maintaining efficient heating. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, approximately 50% of homes in the United States rely on natural gas for heating, underscoring the importance of gas valves in ensuring safe and effective operation.
The design of the gas valve typically includes safety features such as automatic shut-off mechanisms which activate in the event of a malfunction or abnormal pressure levels. The International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials highlights that proper installation and maintenance of gas valves are essential to minimize risks such as leaks, which contribute to hazardous conditions. Additionally, this can lead to increased energy consumption; data indicates that poorly maintained gas systems can account for a substantial portion of excess energy costs, estimated at 20-30% for some households, depending on the maintenance practices employed.
The Role of Gas Valves in Heating Systems
Gas valves play a crucial role in heating systems, acting as the gateway for gas flow from the main supply to the burner assembly. These valves are responsible for controlling the amount of gas that reaches the heating elements, ensuring that the system operates efficiently and safely. By regulating the gas flow, they help maintain the desired temperature within the home while minimizing wastage and reducing the risk of leaks, which can lead to dangerous situations.
In addition to their primary function of regulating gas flow, gas valves also include safety features that protect the entire heating system. Most modern gas valves are equipped with automatic shut-off mechanisms that activate in the event of a malfunction or when the system detects unsafe conditions. This proactive approach enhances the safety of the heating system, providing peace of mind to homeowners. Overall, the role of gas valves in heating systems is essential for functionality, efficiency, and safety, contributing significantly to the effective operation of residential heating solutions.
Gas Valve Performance in Heating Systems
This chart displays the efficiency of different types of gas valves used in heating systems based on their average flow rates (in cubic feet per hour) and their operational reliability ratings (on a scale of 1 to 10).
Types of Gas Valves Used in Heating Applications
Gas valves are essential components in heating systems, playing a critical role in regulating the flow of gas to burners and ensuring efficient operation. There are several types of gas valves used in heating applications, each designed to meet specific environmental and operational needs. The most common types include manual shut-off valves, safety valves, modulating valves, and two-stage valves.
Manual shut-off valves are simple in design, allowing users to control the gas supply manually for maintenance or emergency shut-off purposes. Safety valves, on the other hand, are designed to automatically shut off the gas supply in case of a leak or malfunction, providing essential safety measures in residential and commercial heating systems. Modulating valves adjust the flow of gas based on the temperature requirements, enhancing the system's efficiency and reducing energy consumption. According to the American Gas Association, the implementation of modulating valves can result in a reduction of energy use by up to 30%, making them a popular choice in modern heating applications.
Two-stage valves offer precise control over gas flow, operating at different settings depending on the heating demand. This type of valve is particularly effective in systems that require a varying gas supply, such as multi-zone heating systems. A report from the U.S. Department of Energy indicates that using two-stage valves can significantly improve the overall efficiency of heating systems, leading to lower operational costs and enhanced comfort for users. These advancements in valve technology underline the importance of selecting the right gas valve type for optimal heating performance.
How Gas Valves Regulate Gas Flow in Heating Systems
Gas valves play a crucial role in regulating the flow of gas within heating systems, ensuring both efficiency and safety. According to a report by the American Gas Association, approximately 50% of American households rely on natural gas for heating, making the proper functioning of gas valves vital for comfort and energy conservation. These valves act as control devices, enabling the correct amount of gas to flow to the burner while simultaneously preventing gas leaks.
The regulation mechanisms of gas valves are designed to respond to various operating conditions. For instance, when the thermostat indicates a need for heat, the gas valve opens to allow gas to flow into the heating apparatus. Advanced models may even feature modulating capabilities that adjust the gas flow in real-time based on temperature demands, thereby enhancing energy efficiency. The U.S. Department of Energy has reported that optimized gas flow can lead to energy savings of approximately 10-15% in residential heating, highlighting the importance of maintaining a well-functioning gas valve in any heating system.
What is a Gas Valve and How Does it Work in Your Heating System
| Dimension | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Valve Type | Two-way valve | Controls the flow of gas to the heating system |
| Material | Brass or stainless steel | Durability and resistance to corrosion |
| Connection Type | Threaded or flanged | Ease of installation to the gas line |
| Operating Pressure | 0.3 to 0.5 psi | Safe operation within standard heating systems |
| Safety Features | Automatic shut-off | Prevents gas leaks in case of malfunction |
| Installation Location | Near the heating appliance | Optimizes gas flow control |
| Maintenance | Periodic inspections | Ensures reliable performance |
Common Issues and Maintenance Tips for Gas Valves
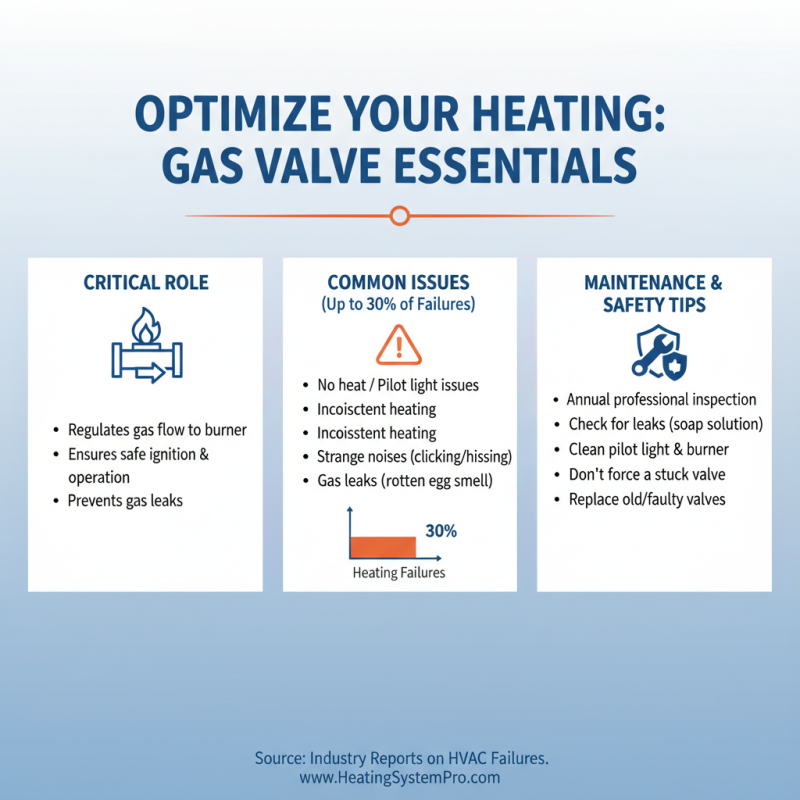
Gas valves are critical components in heating systems, responsible for regulating the flow of gas to burners. Addressing common issues and performing regular maintenance can significantly enhance the efficiency and safety of your heating system. According to industry reports, improper handling or neglect of gas valves is a leading cause of heating system malfunctions, accounting for up to 30% of heating failures in residential properties.
Common issues that homeowners face include valve leaks, improper sealing, and corrosion. Leaks can not only lead to decreased heating efficiency but also pose safety hazards. Regular checks for gas odors and visual inspections can help detect early signs of leaks. Furthermore, corrosion can occur over time, especially in older systems. It is advised to inspect valves for signs of rust or wear and replace them if necessary. Regular servicing by qualified technicians, recommended at least once a year, can help detect these issues early on, potentially saving homeowners from costly repairs.
Maintenance tips for gas valves include ensuring they are clean and free of debris, as obstructions may impede their operation. It’s also essential to verify that all connections are secure and that there are no gaps that could lead to leaks. Keeping the area around the gas valve clear of clutter and moisture can prevent further issues. Following these guidelines not only prolongs the life of the gas valve but also ensures a safe and operational heating system, emphasizing the importance of proactive maintenance.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Importance of Gas Valves in Home Safety and Efficiency
-
Understanding Natural Gas Valves: Essential Guide to Safety and Efficiency in Your Home
-

Why You Should Choose the Right Gas Valve for Your Home Safety
-

10 Essential Flow Control Tips to Optimize Your Workflow and Productivity
-

2025 Top Trends in Automatic Valves for Industry and Home Use
-

2025 Guide: How to Choose the Perfect Dresser Utility for Your Space
