How to Effectively Manage Pressure Control in Industrial Applications?
Effective pressure control is critical in industrial applications. It impacts safety, efficiency, and product quality. Companies rely on precision to manage pressure in various processes. The challenge lies in the varying conditions and technologies involved. Different industries face distinct pressure requirements, adding complexity to management practices.
For instance, a chemical plant needs precise pressure control to avoid hazardous situations. In contrast, a food processing facility may prioritize maintaining product consistency. Each scenario demands specific strategies. Real-time monitoring systems play a vital role. However, implementing these systems can reveal weaknesses in existing protocols. There may also be unexpected costs associated with upgrades.
People must recognize that pressure control is not foolproof. Equipment can fail, and human error can occur. Regular training and system evaluations can mitigate these risks. Yet, no system is impervious to mistakes. A reflective approach is essential. Understanding these limitations can lead to improved methods. Discovering better ways to manage pressure is an ongoing journey in industrial settings.

Understanding the Importance of Pressure Control in Industrial Settings
Pressure control plays a critical role in industrial settings. It influences operational safety, efficiency, and product quality. Proper management can prevent accidents and equipment failures. A small mistake in pressure regulation can lead to disastrous results. Employees must be trained to recognize signs of pressure anomalies. Awareness is key in complex systems with multiple variables.
In many cases, companies invest heavily in technology. Yet, they may overlook basic practices. Regular maintenance can be neglected. Over time, equipment may become less reliable. This highlights the need for routine checks and balances. Automated systems can help, but human oversight remains essential. Without careful monitoring, even advanced systems may fail unexpectedly.
Employees must also understand the pressure variations that occur in production. Pressure changes affect the materials used and product consistency. Training sessions can enhance understanding among staff. However, practical assessments are often lacking. This creates a gap in knowledge that can hinder effective pressure management. Collectively, organizations can improve their processes by addressing these overlooked details.
Pressure Control in Industrial Applications
This bar chart illustrates various pressure levels (measured in psi) across different types of industrial applications. Effective management of these pressure levels is crucial for maintaining operational safety and efficiency in industrial settings.
Key Components of Pressure Control Systems in Industrial Applications
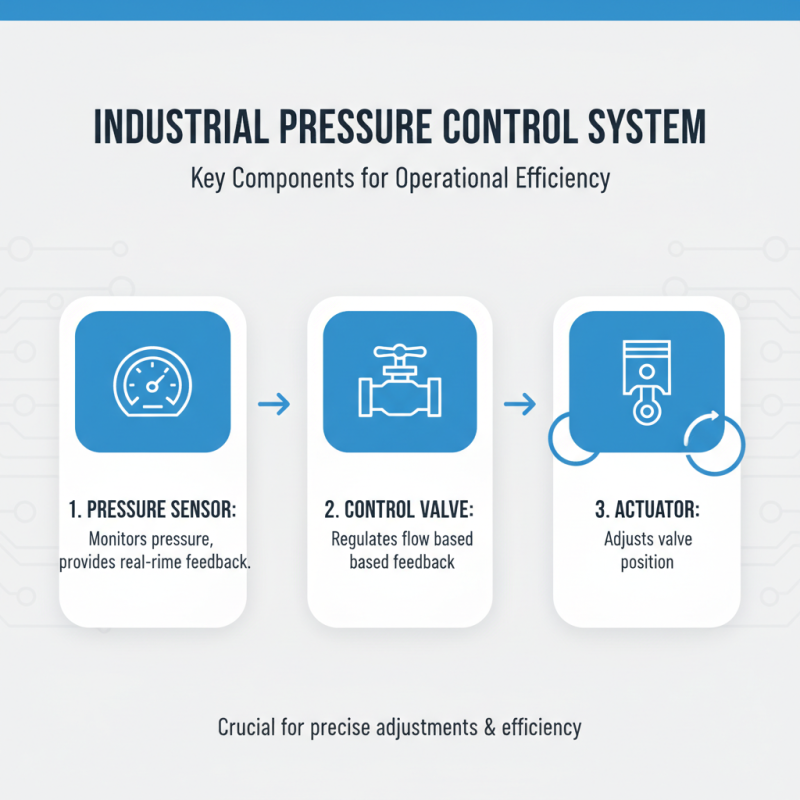
Effective pressure control is crucial in various industrial applications. Understanding the key components of pressure control systems can significantly enhance operational efficiency. These systems typically consist of pressure sensors, control valves, and actuators. Pressure sensors monitor the levels accurately, providing real-time feedback. Without precise readings, adjustments may lead to errors and inefficiencies.
Control valves play a vital role in regulating pressure within the system. They can adjust flow rates and maintain desired pressure levels. It’s important to select the right type of valve for specific applications. Improper valve selection might cause pressure fluctuations, leading to equipment wear or failure. Actuators, often overlooked, are essential. They translate control signals into mechanical motion, ensuring timely responses to pressure changes.
Moreover, regular maintenance of these components is necessary. Neglected systems can operate inefficiently, leading to wastage and increased costs. Continuous monitoring allows for early detection of potential issues. Identifying problems before they escalate can save time and resources. Reflecting on these aspects ensures pressure control systems work optimally. Balancing efficiency with accurate readings creates a reliable operation.
Strategies for Monitoring and Maintaining Pressure Levels Effectively
In industrial applications, managing pressure is vital. Effective monitoring and maintenance can lead to reduced downtime and increased efficiency. A recent report from the International Society of Automation notes that about 30% of all industrial accidents are pressure-related. This underlines the need for stringent monitoring systems. Regular equipment checks and data analysis can prevent pressure anomalies that might lead to catastrophic failures.
Monitoring pressure levels requires a mix of technology and human oversight. Implementing real-time data analytics can help organizations track fluctuations immediately. According to the World Pressure Control Association, industries that embraced such systems reported a 25% decrease in pressure-related incidents. However, reliance on technology can lead to complacency. Employees must remain trained in manual checks to complement automated systems.
Pressure control is not foolproof. Mistakes happen, such as misreading gauges or overlooking maintenance schedules. These can result in costly errors. Regular audits and revisiting strategies are essential. They foster a culture of safety and awareness. In industrial environments, maintaining optimal pressure isn’t just about technology; it's about human vigilance.
Common Challenges in Pressure Control and How to Address Them
Managing pressure control in industrial applications can be complex. One major challenge is fluctuations in process conditions. Temperature changes or inconsistent flow rates can all impact pressure stability. For instance, a sudden spike in temperature may cause pressure to increase unpredictably. Operators need to remain alert to these variations to ensure system integrity.
Another common issue is equipment failure. Valves and sensors can wear out over time, leading to inaccurate readings. A malfunctioning pressure gauge, for example, could misinform operators about the actual pressure level. Regular maintenance is essential, but it often gets overlooked. Neglecting this can lead to costly downtime. Operators should develop a routine check system that is easy to follow.
Communication among team members can also pose challenges. Misunderstandings about pressure setpoints can lead to mistakes in operation. Clearly defined protocols can help mitigate this risk. Teams should have access to updated information and be trained regularly. It’s crucial to address these challenges proactively. Without proper management, even minor issues can escalate into significant problems.
Best Practices for Implementing Pressure Control Solutions in Industry
Pressure control is vital in industrial applications. Managing it effectively can prevent costly failures. One key practice is regular maintenance. Equipment should be inspected routinely. Gaskets, valves, and gauges must function correctly. Neglecting these elements can lead to dangerous situations.
Training staff is equally essential. Operators should understand the systems they control. They need to be aware of pressure thresholds. This awareness helps in identifying issues before they escalate. Frequent workshops can reinforce this knowledge. Encouraging a culture of safety is paramount.
Data analysis plays a crucial role too. Monitoring pressure metrics can reveal patterns. Unexpected spikes or drops indicate problems. Yet, many systems lack effective data integration. Risk can increase when data is siloed. Addressing these gaps may seem daunting but is necessary for improvement. Exploration of better solutions can lead to enhanced performance.
How to Effectively Manage Pressure Control in Industrial Applications? - Best Practices for Implementing Pressure Control Solutions in Industry
| Aspect | Best Practices | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Maintenance | Implement scheduled inspections and servicing | Reduces downtime and extends equipment lifespan |
| Training Personnel | Provide regular training on pressure control systems | Enhances safety and operational efficiency |
| Data Monitoring | Utilize sensors and automate data collection | Enables real-time adjustments and predictive maintenance |
| System Upgrades | Invest in modern pressure control technologies | Increases accuracy and reduces energy consumption |
| Compliance Audits | Regularly review systems against industry standards | Ensures regulatory compliance and avoids penalties |
Related Posts
-

2025 Top Trends in Automatic Valves for Industry and Home Use
-

2025 Guide: How to Choose the Perfect Dresser Utility for Your Space
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Automatic Valves in Industrial Applications
-

What is a Safety Valve and How Does It Work?
-

Maximizing Efficiency with Asco Solenoids in Modern Automation Systems
-

2025 Top 5 Control Valve Trends Driving Efficiency in Industrial Applications
